Behind the Scenes:The Sequential Stages of 3D printing
3D PRINTING JUNCTURES
The 3D printing process typically involves several stages, although the specific steps may vary depending on the technology and materials used. Here are the major steps involved in the 3D printing process:
1. Design:
The design phase begins with the development of a 3D model for the object, employing various resources such as computer-aided design (CAD) software, 3D scanners, photogrammetry, 3D printing pens, generative design, parametric design, and scripting. This digital design file, commonly known as the blueprint, acts as the initial stage in the 3D printing process.
2. Pre-processing:
Before initiating the 3D printing process, it's essential to prepare the 3D model in accordance with your envisioned design, as well as the specific 3D printing technology and chosen material. This preparation involves various tasks, including segmenting the model into distinct layers, establishing support structures, and configuring a range of settings, including print parameters.
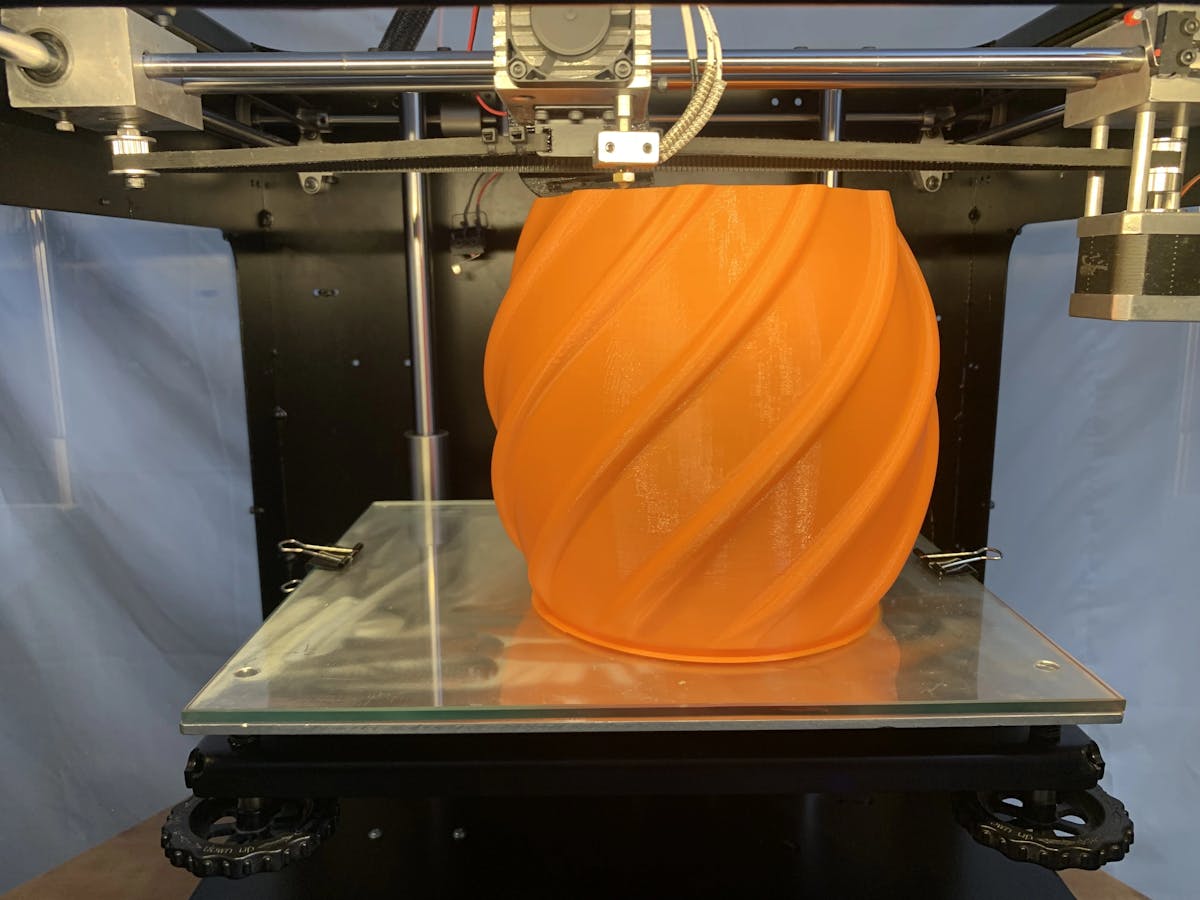
3. Printing:
The 3D printer executes instructions derived from the pre-processed model, crafted earlier, to construct the object incrementally, layer by layer. The specific printing technique employed, whether it involves extruding filament, curing resin, or sintering powder, can vary depending on the chosen technology.
4. Post-processing:
After the printing phase, the object typically undergoes post-processing aimed at enhancing its overall quality, visual appeal, or functionality. This stage commonly involves tasks like the removal of support structures, sanding, painting, or the application of additional finishing methods.
5. Inspection and Quality Control:
A thorough examination of the printed object is conducted to verify its alignment with the specified requirements and quality benchmarks outlined by the client. This inspection encompasses various aspects, including visual scrutiny, dimensional measurements, functional testing, and additional checks as necessary.
6. Assembly (if necessary):
When dealing with objects composed of multiple components or intricate geometries, assembly is conducted in a dedicated assembly section following the printing phase. Here, parts are interconnected employing methods such as adhesives, screws, soldering, or other suitable fastening techniques.
7. Finishing and Packaging:
This marks the concluding phase, encompassing an array of supplementary refinements such as polishing, coating, or labelling, all aimed at elevating the quality and surface finish of the objects. Once these finishing touches are applied, the finalized objects are meticulously packaged and made ready for distribution, a task overseen by the company's distribution team.