
Revolutionizing Manufacturing- The Power of Binder Jetting 3D Printing
Introduction
Binder Jetting is a powerful and versatile additive manufacturing technology that offers a cost-effective and rapid production method of 3D printing. Due to its wide material compatibility, including metals, ceramics, and sand, powder self-support and high-volume production, Binder Jetting is considered to be one of the most promising 3D printing technologies. These advanced printers are capable of producing highly detailed and complex geometries with remarkable efficiency.
A Binder Jetting machine 3D prints the model by selectively depositing a liquid binding agent onto a layer of powder material. The binding agent acts as an adhesive, selectively deposited onto a bed of powder material to bond the particles together. The process is similar in working to a classical inkjet 2D printer, however the Binder Jet builds a 3-dimensional object by “slicing” the model and printing layer by layer.
How does a Binder Jet print a 3D model?
First we need to design and slice our 3D model before printing. In general, you can follow these steps:
- Create your 3D model using common 3D CAD (Computer Aided Design) design software such as Fusion360, Solidworks, Blender, etc.
- Export the 3D model in a format supported by the slicing software used with your 3D printer. Common formats include STL, OBJ, or 3MF
- Use the slicing software to ”slice” the 3D model into thin horizontal layers. This process generates the toolpaths and instructions (G-code) necessary for the 3D printer.
- Load the sliced file into the 3D printer’s control interface and start the printing process.
For more beginner friendly information, you can visit 3D Printing Unveiled: A Beginner's Guide. To read further on slicing software.
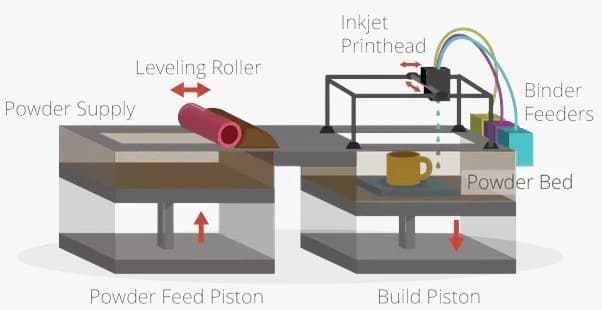
Schematic of a typical binder jetting 3D printing process. Image via Quora
The Binder Jet machine prints your 3D model by the following steps:
- First, a recoating blade or head spreads a thin layer of powder over the machine’s build platform.
- Next, the printhead (a carriage with inkjet nozzles, similar to those used in desktop 2D printers) precisely jets the binding agent into the powder according to the part’s geometry.
- When the binder layer is complete, the build platform lowers, and the re-coater spreads a fresh layer of powder across the platform and top of the part being printed.
- The printhead binds another layer and this process repeats until the build is complete. Based on the material, some amount of postprocessing might be required.
Why do we need Binder Jetting?
- Binder Jetting is relatively productive and cost-effective compared to other 3D printing processes. It can run unattended, offering an automated way to produce a range of components with minimal human interference.
- Rapid mass production: 3D core parts are supported by unused powder and can therefore be stacked in three dimensions, allowing for efficient nesting to produce more parts per run (high volumetric output).
- Speed and precision: It's up to 10 times more economical than selective laser sintering (SLS) or selective laser melting (SLM) and offers relatively large build sizes of up to 800 x 500 x 400 mm.
- Material diversity: Binder Jetting offers remarkable material diversity, accommodating a wide range of powders suitable for various applications. This includes metals, ceramics, polymers, and even composite materials.
- Powder reuse: Without the influence of heat in the build chamber, unused powder doesn't degrade and can be recycled back into the process, so effectively powder untouched by the binder is essentially the same coming out of the build envelope as it was going into the printer.